V-belt is a crucial component of machinery used to transmit power between different parts of the machine. These flexible elements are usually made of rubber or synthetic materials like neoprene or polyurethane. V-belt is a trapezoidal shape that ensures a secure fit into the shaft’s sleeves. These belts are designed by compressing various fibrous tensile cords for strength and longevity.
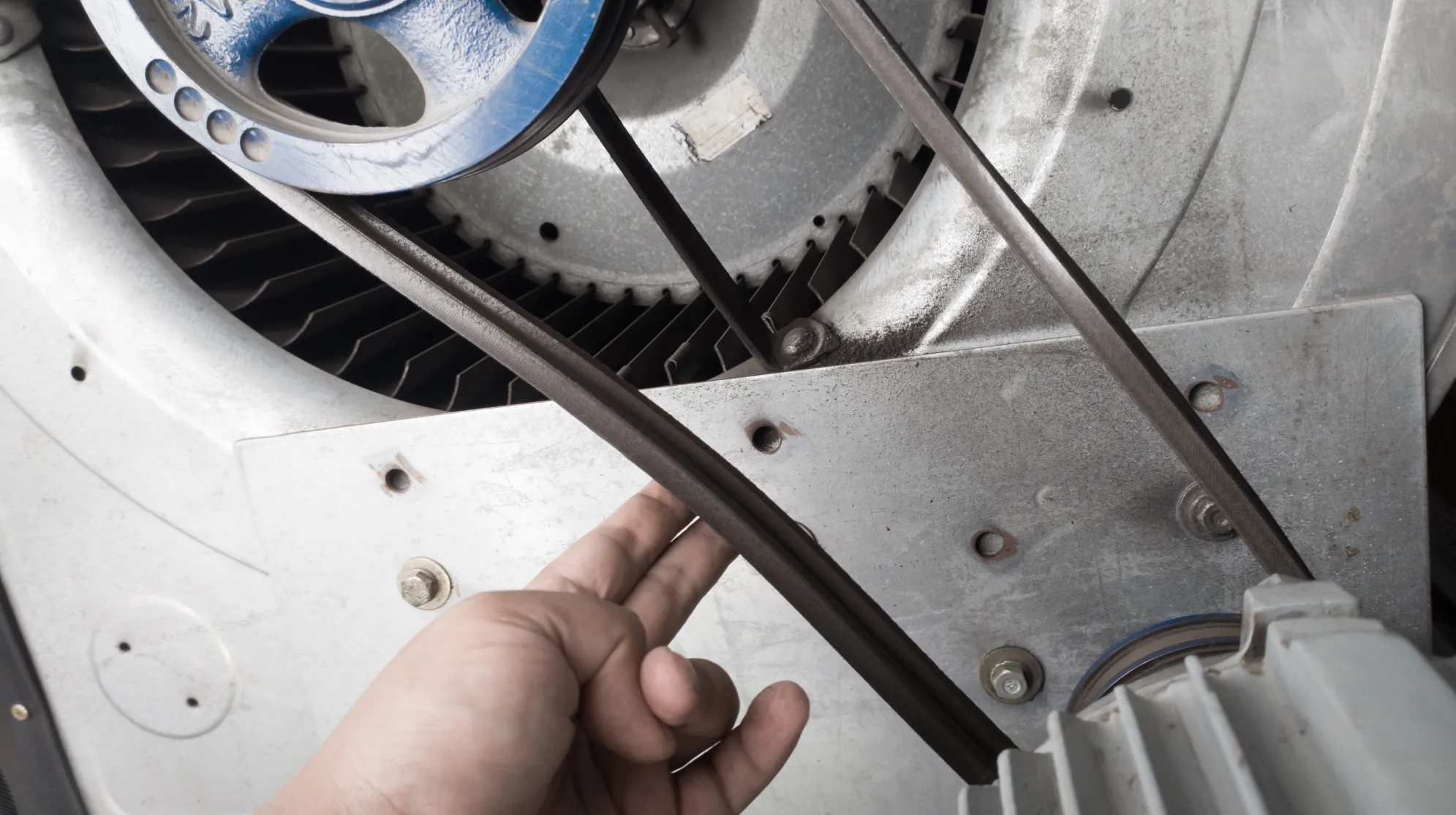

V-belts, due to their trapezoidal cross-sectional shape, provide a better grip on the pulley than flat belts. The V-shaped wedges into the pulley groove lead to better traction and reduced slippage. These mechanical belts are widely used in industrial machinery, automotive engines, agriculture equipment, and more.
The Role of V-Belts in Machinery
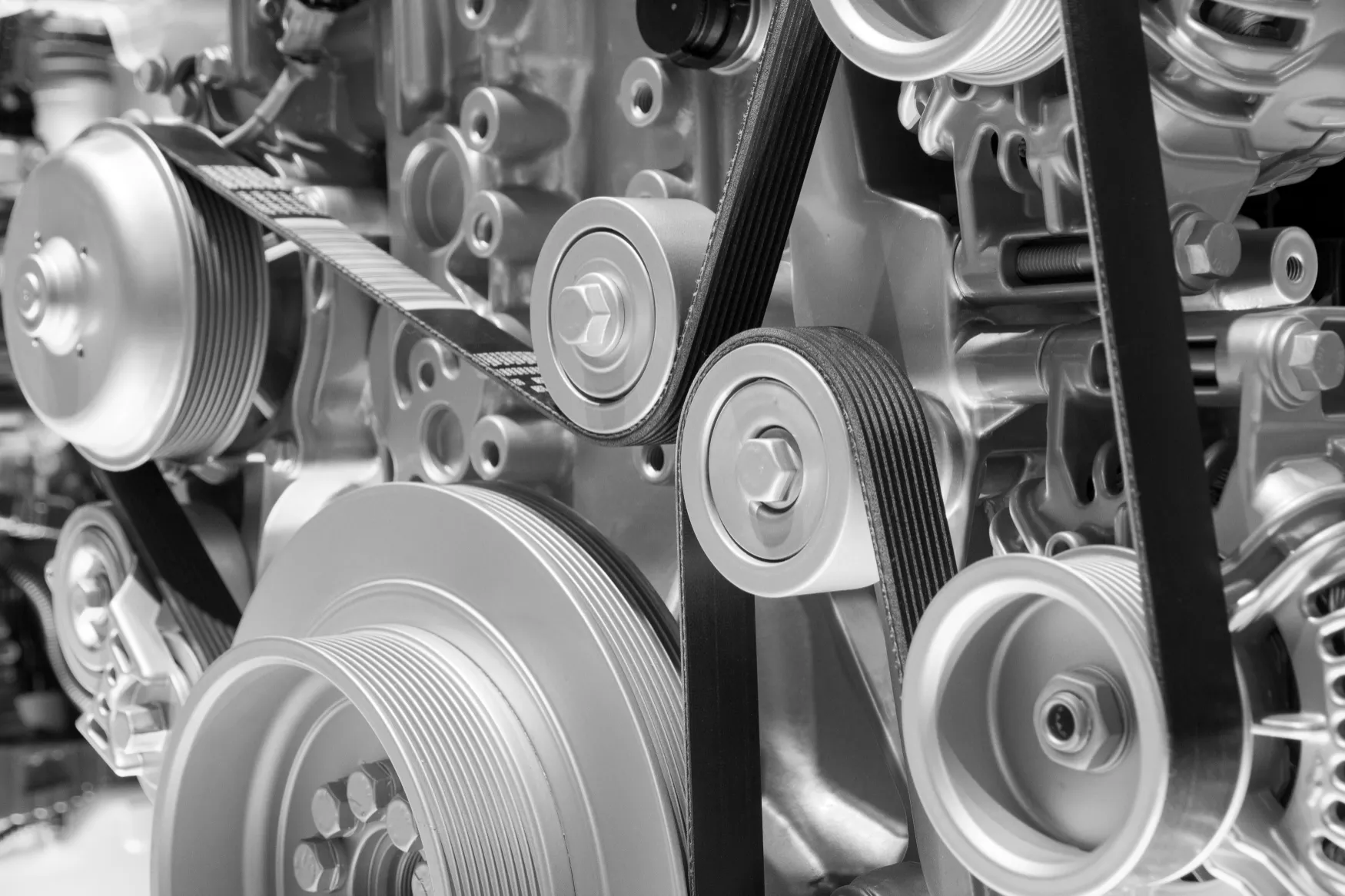
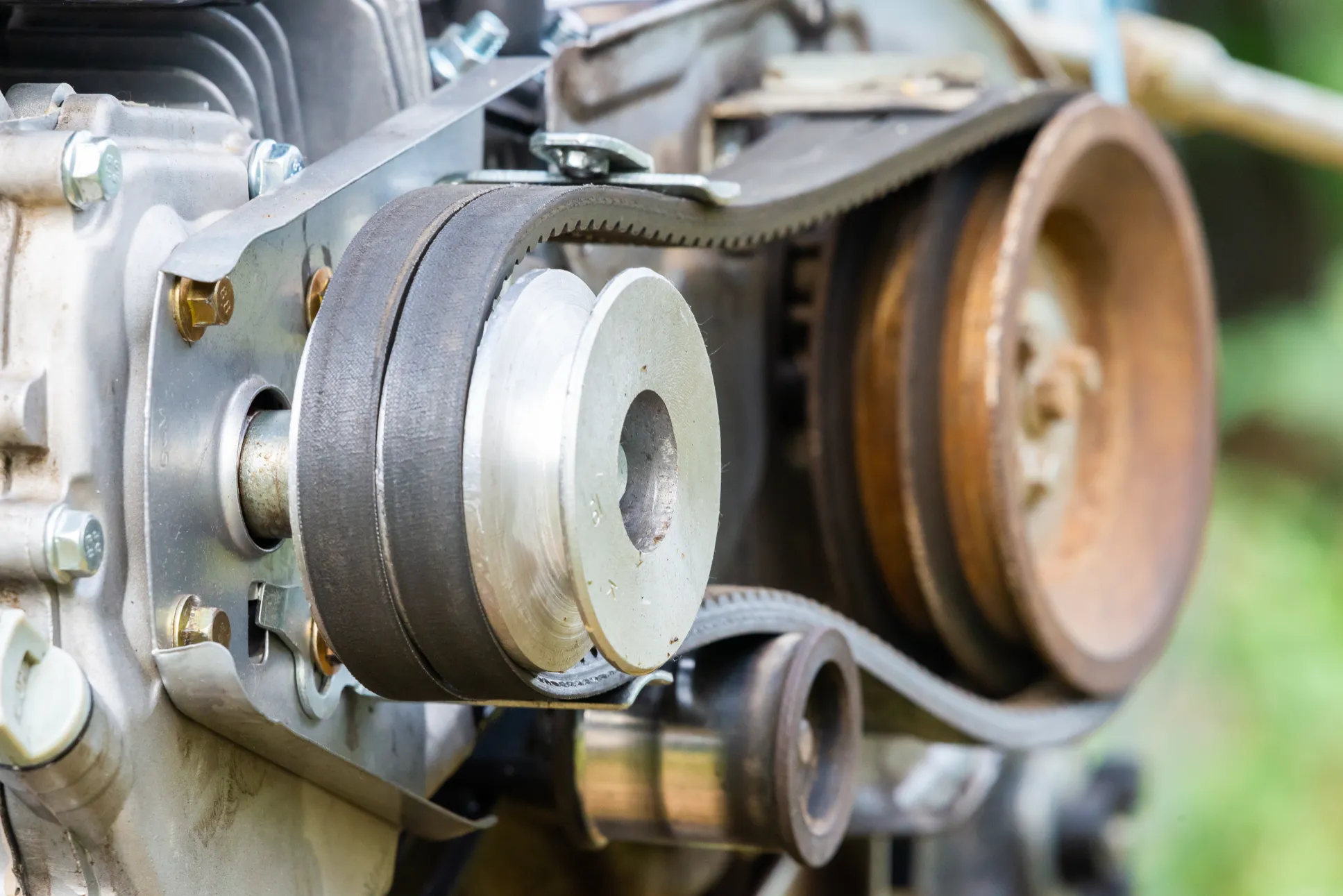

The efficiency of any machinery doesn’t just depend on the big visible parts like motors or engines but it also depends on smaller components like bearings, bushings, pulleys, v-belts, and more. One such important component of these machines is the V-belt.
- Power Transmission: These belts are crucial for transmitting power from one rotating component of the machinery to another. In conveyor systems v-belt connects the motor with a drive pulley which further moves the conveyor belt.
- Maintain Tension & Alignment: V-belts also play a role in maintaining constant tension and alignment with the pulleys which helps prevent slippage and ensure smooth power transfer.
- Shock Absorption: These flexible belts help damp vibrations and absorb shocks caused due to sudden jerks or uneven loads. In agricultural machinery, v-belts play a key role in reducing jerks and protecting the drive system.
- Maintains Efficiency: V-belts help maintain efficiency by minimising slippage and reducing energy loss.
Common Causes of V-Belt Failure
Various factors may lead to premature failure of these mechanical belts including incorrect tension, misalignment of pulleys, environmental factors and more. Some of the most common causes of v-belt premature failure

- Improper Tensioning: Improper tensioning of the v-belt, i.e. too tight tensioning can strain the bearings and the belt, while too loose tension can lead to slippage & heat buildup resulting in quick wearout or breaking of the belt.
- Misaligned Pulleys: Unaligned pulleys can cause the belt to twist and wear unevenly leading to increased vibration, noise, and premature failure.
- Excessive Heat: The V-belt may get worn out quickly due to excessive heat causing the belt material to weaken and degrade weakening the belt structure and resulting in belt failure.
- Wrong Belt Type: V-belts are not one-size-fits-all and one size is not suited for all application types. Using the wrong belt type can reduce efficiency and lifetime.
- Other Factors: Exposure to oils, grease, chemicals, and others can degrade the belt’s rubber and can even cause the rubber to slip resulting in premature failure.
V-belt is a widely used mechanical component, from applications in big mechanical systems like conveyors, compressors, crushers, and pumps these are also used in fans, mixers, screens, and more. However, selecting the right V-belt is absolutely critical for both performance and reliability.
Types of V-Belts
There are various types of v-belts designed for different applications. Some of the common types of v-belts include:
- Standard or Classical V-Belt: This type of v-belt is also referred to as classical, standard or conventional belts. Standard v-belt is used in a wide range of general-purpose machinery like pumps, compressors, etc. The dimensions of standard v-belts are designated as Y, Z, A, B, C, D, and E.
- Wedge V-Belt: Wedge v-belt is designed for high-speed and high-torque transmission. They can operate 1.5 to 2 times the load of classical v-belts. Wedge v-belt is commonly fitted in crushers, mixers, industrial gearboxes, and more.
- Narrow V-Belt: Narrow v-belt as the name implies has a narrower profile but transmits more power than classical belts. Narrow v belts are ideal for compact & high load systems including heavy-duty fans, HVAC systems, industrial drives, etc.
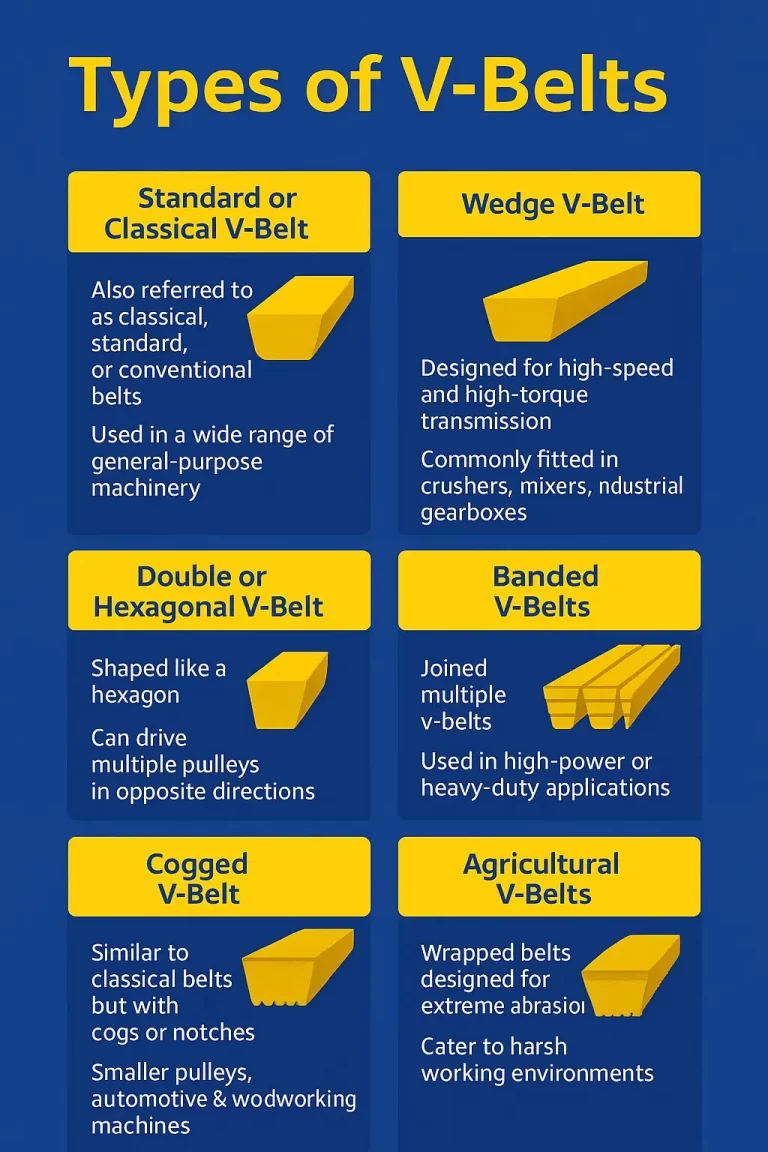
- Double or Hexagonal V-Belt: This type of v-belt is shaped like a hexagon and is designed to transmit power from both sides of the belt. A double v-belt can drive multiple pulleys in opposite directions. Textile machinery and agriculture equipment are equipped with this type of belt.
- Banded V-Belts: Also known as joined v-belts multiple v-belts joined together. This type of v-belt is used in high-power or heavy-duty applications like stone crushers, large fans, and more.
- Cogged V-Belt: Cogged v-belts are similar to classical belts but they have cogs or notches at the bottom side. Smaller pulleys, automotive, and woodworking machines are usually equipped with cogged v-belts.
- Agricultural V-Belts: Agricultural belts are wrapped belts designed for more extreme abrasion from dust, sand, grains, and more. This type of belt is made of durable polyurethane blends to cater to harsh working environments.
Factors to Consider While Selecting V-Belts
Now, when it comes to longevity & durability several factors play a key role in enhancing efficiency and avoiding premature failure. Also, finding the right fit guarantees performance, durability, and safety. Some of the key factors to consider include.
| Factors | What to Consider |
| Load Requirements | Power to be transmitted, i.e. heavier tabs require stronger belts. |
| Speed in RPM | For higher speed, belts that support higher speed are required. Like narrow or wedge belts. |
| Centre Distance | The distance b/w the pulleys affects belt length & tension settings |
| Operating Environment | Belts made of higher grade must be chosen if there is exposure to dust, oil, moisture, etc. Ex: agricultural v-belt. |
| Space | V-belts must be chosen based on application space, if space is limited narrow V-belts are preferred. |
| Temperature | Choose belts based on operating temperature, if operating temperature is more choose belts made to support such temperature. |
V-Belt Installation Techniques
Proper installation of a v-belt is essential for ensuring long belt life, proper tension, and safe operation. The installation of v-belts involves the steps mentioned below:
Step 1 – Check Pulleys: The first step in the installation is to check the pulleys thoroughly. The process involves identifying signs of damage and detecting worn-out parts. A damaged or worn-out pulley component may reduce v-belt life, cause slippage of the belt, reduce power transfer, and lead to vibrations.
Step 2 – Check Alignment: Check the alignment using a straight edge or laser alignment tool. Misalignment can lead to premature wear.
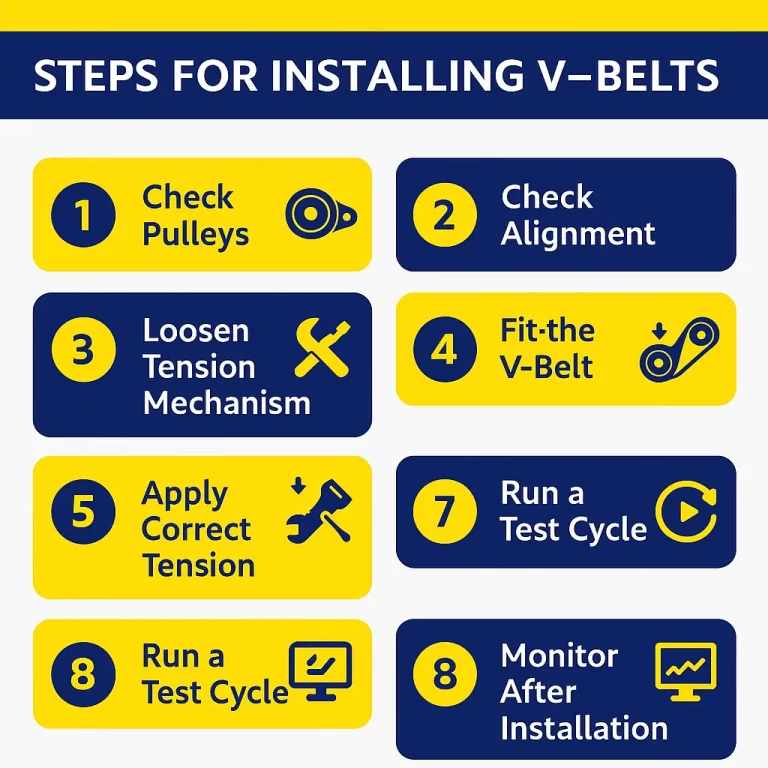
Step 3 – Loosen Tension Mechanism: Loosen the mounting bolts or tensioner to allow belt fitting.
Step 4 – Fit the V-Belt: Place the belt into the pulley groove without twisting or stretching.
Step 5 – Apply Correct Tension: Use a belt tension gauge or follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for correct tension and ensuring safety.
Step 6 – Tighten & Recheck: Secure the bolts and tensioners and re-check the alignment and tension.
Step 7: Run a Test Cycle: Turn the power on and run it briefly. Check for unusual sounds, vibrations, and belt movements.
Step 8: Monitor After Installation: Recheck the belt tension after a few hours of operation, the belt may require tightening as it often stretches slightly.
Routine Maintenance Tips to Extend V-Belt Life
Periodic maintenance of v-belts is key to keeping machinery efficient, reducing downtime, and extending belt life. The maintenance procedure involves
- Visual Inspection: Visual inspection can be done weekly or as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. The process involves inspecting for cracks, fraying, glazing, etc.
- Check Belt Tension: Belt tension can be checked every 2 weeks or as per the manufacturer guidelines by using a tension gauge or deflection method.
- Check For Alignment: Alignment can be checked monthly using a straight edge or laser.
- Clean the Drive Area: The drive area must be cleaned regularly including removing dust, oil, debris, and chemical buildup.
- Listen to Noise: Check for unusual sounds during operation as it may indicate slippage or misalignment.
- Check For Vibration: Vibrations during operations can be checked at monthly intervals, excessive vibration may indicate a loose belt or misalignment of components.
- Replace: If there are signs of wear, cracks or damage it is recommended to replace the belt.
Common Causes of V-Belt Failure
V-belt failure can result from several factors, improper tension and misalignment are the most frequent causes of V-belt failure. Some other causes of v-belt failure include:
- Improper Tension
- Pulley Misalignment
- Worn Pulleys
- Wrong Belt Size
- Contamination
- Overheating
- Aged/Cracked Belts
When to Replace a V-Belt?
Replacing a v-belt is essential for maintaining the smooth, safe, and efficient operation of the machinery. V-belt should be generally replaced every 1 to 3 years or as per the manufacturer’s guideline or when signs of wear and damage like cracks, missing chunks, or squealing are present. A few factors that determine if a V-belt needs replacement include:
- Age: V-belts should be replaced every few years, especially if there’s heavy usage or extreme temperatures.
- Visual Inspection: If there are signs of damage, cracks, or excessive wear.
- Squealing Noise: A squealing or chirping noise could also indicate that the belt needs replacement.
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: The belt should also be replaced according to the interval recommended by the manufacturer.


















