Summary
At NBC Bearings, we understand that reliable motion starts with high-quality components. Tapered roller bearings are at the heart of countless machines across automotive, aerospace, and heavy industries. In this article, we explore their design, benefits, applications, and maintenance best practices — helping you get the most out of these essential components while ensuring long-term performance and operational efficiency.Introduction
In every industry where motion and precision matter — from automotive wheels to heavy-duty industrial gearboxes — one component consistently plays a critical role: the tapered roller bearing. These bearings are designed to manage both radial and axial loads efficiently, ensuring machines perform with consistency, stability, and reliability. At NBC Bearings, we understand how vital it is to select and maintain the right bearing for the right application. In this article, we’ll explore what tapered roller bearings are, why they are so widely trusted across industries, and how proper maintenance can significantly extend their service life.Understanding Tapered Roller Bearings
A tapered roller bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses conical rollers and matching raceways. This geometry allows it to handle combined loads — both radial and axial — while maintaining smooth, low-friction operation.Design Overview
Each bearing consists of four key parts:- Inner ring (cone)
- Outer ring (cup)
- Tapered rollers
- Cage to maintain roller spacing
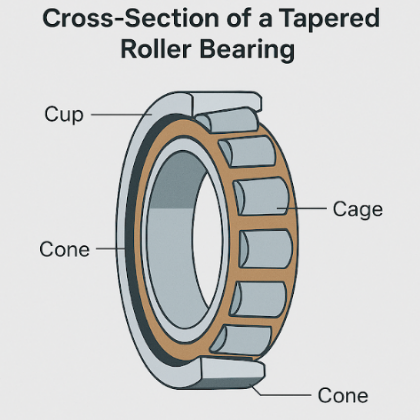 As the bearing rotates, the tapered rollers roll along the raceways, distributing loads evenly. This minimizes friction, reduces heat generation, and provides higher stability under demanding conditions.
As the bearing rotates, the tapered rollers roll along the raceways, distributing loads evenly. This minimizes friction, reduces heat generation, and provides higher stability under demanding conditions.
Types of Tapered Roller Bearings
- Single Row: Supports radial and single-direction axial loads.
- Double Row: Handles axial loads in both directions.
- Four Row: Ideal for heavy-duty operations such as steel rolling mills and rail applications.
Key Benefits
- High Load-Carrying Capacity – Efficiently supports both radial and thrust loads simultaneously.
- Enhanced Durability – Withstands heavy shocks and impacts with long service life.
- Low Friction & Heat Generation – Improves energy efficiency and reduces wear.
- Application Versatility – Available in multiple configurations for diverse industry needs.
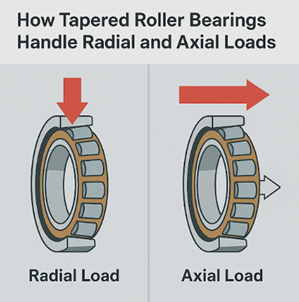
Applications Across Industries
Automotive:
Used in wheel hubs, transmissions, and differentials, tapered roller bearings ensure reliable performance and long vehicle life.Aerospace:
In aircraft engines, landing gear, and control systems, these bearings deliver precision and endurance under extreme conditions.Industrial Manufacturing:
Gearboxes, conveyors, and heavy machinery depend on them for smooth, continuous operation.Railways & Heavy Transport:
Double and four-row bearings handle massive loads in locomotives, freight cars, and bogies.Agricultural Equipment:
Designed to perform under harsh field conditions, ensuring stability and consistent performance in tractors and harvesters.Common Issues and Maintenance Best Practices
Even the best bearings can experience premature wear if not maintained properly. Below are the most common issues and preventive measures:Common Issues
- Improper Lubrication: Leads to overheating and surface damage.
- Contamination: Dirt, moisture, or metal particles reduce bearing life.
- Misalignment: Causes uneven load distribution and vibration.
- Overloading: Exceeding design limits results in fatigue and cracking.
Maintenance Tips
- Lubrication: Always use the recommended grease or oil, and re-lubricate at intervals suitable to the operating conditions.
- Installation: Follow correct procedures and avoid using force during assembly.
- Inspection: Regularly check for noise, vibration, or temperature changes.
- Clean Environment: Keep bearings and housings free from contaminants.
- Timely Replacement: Prevent unplanned downtime by replacing bearings before the end of their service life.


















