Bearings are essential components that keep our world rolling smoothly. These mechanical wonders reduce friction which is the main factor which helps in the smooth operations of a vast variety of movable devices and machinery. From your skateboard wheels to the wheels of a high-speed train to function, the simple act of opening your refrigerator door to the complex processes inside a jet engine, each of these are dependent upon bearings for their efficiency. In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of bearings, breaking down the different types and their everyday applications.
Types of Bearing for Your Application
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings
- Cylindrical Roller Bearings
- Spherical Roller Bearings
- Needle Roller Bearings
- Tapered Roller Bearings
Rolling into Bearings 101
Before we dive into the diverse world of bearings, let’s get our bearings straight (pun intended!). Imagine trying to move your furniture across the room without wheels or bearings. It would be an arduous task! Bearings are mechanical devices that reduce friction between moving parts in a machine, allowing them to move more smoothly and efficiently. They come in various shapes, sizes, and designs, each serving a specific purpose in the grand machinery of our world. Bearings are impacting everything in our lives but we are not aware of where and how. From industrial machines to the tiny wheels on a shopping cart, bearings are everywhere.
Ball Bearings: Round and Rolling like BB-8
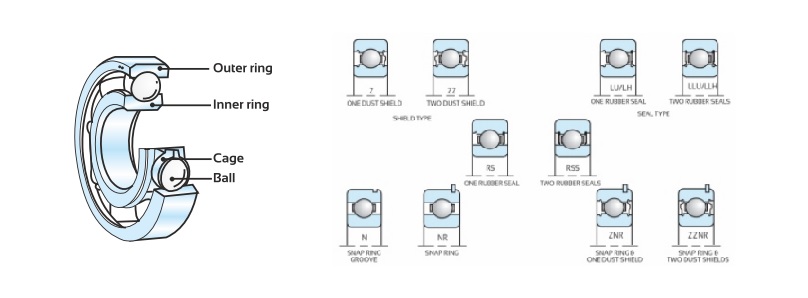
If you’re a Star Wars fan, then ball bearings would be as active and reliable as the great BB-8, the lovable spherical droid. Ball bearings consist of small, round balls housed in a circular raceway. Picture a ball pit at a children’s play center, but now imagine these balls are precision-engineered and made of metal. Ball bearings are all about reducing friction by using small metal balls between two surfaces. They are adept at handling radial and thrust loads where smooth rotation is essential.
- Skateboards: The coolest skateboarding legends owe a lot to ball bearings. They keep skateboard wheels spinning smoothly, making those incredible tricks possible.
- Electric Fans: Ever wondered why your fan rotates so effortlessly? Ball bearings are the answer, ensuring your room stays cool without any annoying squeaks.
- Maintenance: Carefully handle bearings and store them in a clean and dry place. Check housing and shaft for dirt or damage. Avoid direct heat and lubricate regularly.
Roller Bearings: The Swiss Roll of Bearings
Imagine a delicious Swiss roll cake, and now imagine them made in durable metal that use cylindrical rollers to distribute load more evenly. That is how a roller bearing works. They come in various designs, including cylindrical, tapered, and needle rollers, each tailored for specific applications. Roller bearings take the principle of ball bearings to the next level. Instead of small balls, they use cylindrical rollers to reduce friction. This design handles heavier loads and is commonly seen in:
- Automobiles: Roller bearings support various components in your car, like the wheels, transmission, and engine. Without them, your road trip would be a bumpy ride.
- Conveyor Belts: At airports, roller bearings play a crucial role in moving luggage smoothly from one place to another.
- Maintenance: Carefully handle bearings and store them in a clean and dry place. Check housing and shaft for dirt or damage. Avoid direct heat while mounting the bearing and lubricate regularly.
Tapered Roller Bearings: The Conquerors of Axial Loads
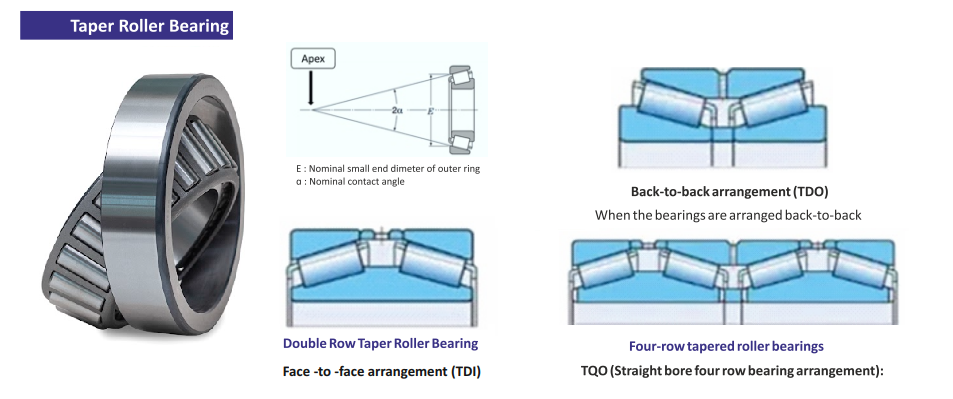
Tapered roller bearings are the superheroes of bearings who can handle axial (thrust) loads in addition to radial loads. They ensure smooth rotation, especially during sharp turns. Much like how Batman’s cape helps him glide gracefully through Gotham’s skies, tapered roller bearings help vehicles maneuver with ease. But in the bearings universe tapered roller bearings can be considered the multitaskers. These bearings are found in:
- Trucks and Heavy Machinery: Tapered roller bearings support the enormous weight of trucks and construction equipment, ensuring they don’t buckle under the pressure.
- Automobiles: Steering wheels of passenger vehicles.
- Washing Machines: Even household appliances benefit from these bearings, ensuring your clothes get a thorough wash without any hiccups.
- Maintenance: Proper servicing is required to chemically clean, and air dry bearings. The roller, cage, rings, and race must be carefully examined for wear, pitting, or discoloration, and then repacked with the proper grease.
Spherical Bearings: Bearing with an Angle
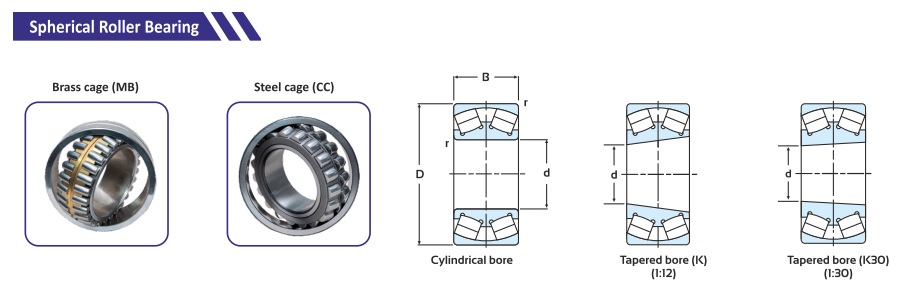
In terms of versatility spherical bearings are the most valuable players for the bearings team. These bearings can tilt, swivel, and adapt to angular misalignments, quite like gymnasts in the bearing universe, bending and flexing to maintain contact and distribute loads evenly. These bearings can handle misalignment and accommodate angular motion, making them versatile in applications such as:
- Astronomy: Telescopes use spherical bearings to track celestial objects across the night sky. This flexibility ensures astronomers don’t miss out on the wonders of the universe.
- Robotics: Spherical bearings are vital in robotics, allowing robots to move precisely and adapt to changing conditions.
- Maintenance: Routine inspection, timely lubrication for reduced friction, alignment checks and temperature monitoring while avoiding humidity will help scale-up the lifetime of the bearing.
Needle Bearings: Small But Mighty
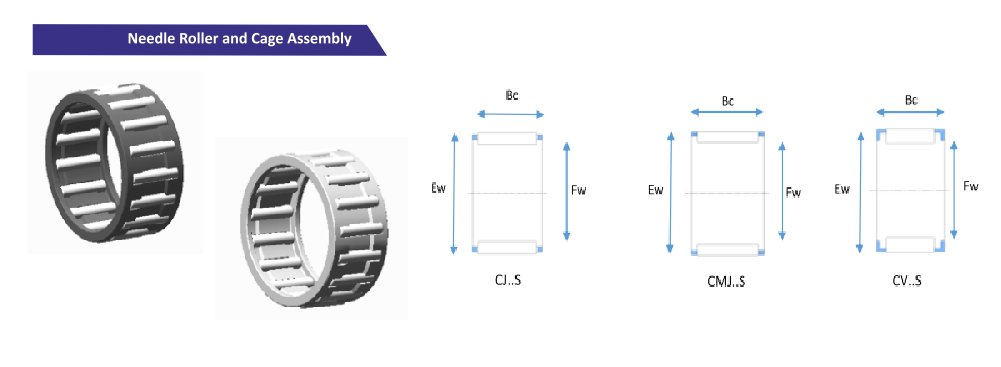
Needle bearings are the slender athletes among bearings, known for their high load-carrying capacity in a compact design. They may look unassuming, but they pack a powerful punch in applications where space is limited, like Ant-Man who shrinks to navigate tight spaces, in cramped quarters. Their slender cylindrical rollers make them ideal for high radial loads. They find their niche in:
- Motorcycles: Motorcycle engines rely on needle bearings for smooth operation, ensuring that you enjoy the open road without any interruptions.
- Textile Industry: The precision of needle bearings is essential in textile machinery, helping to weave fabrics flawlessly.
- Maintenance: Protect needle bearings from contaminants which means sealed and secured from dirt, dust, and moisture. Ensure that seals or shields are intact and functional. Check for any misalignment or unusual noise during operation as this can bring down the productivity of the bearing in the long run.
Plain Bearings: The Silent Workers
While rolling bearings get most of the spotlight, plain bearings work silently behind the scenes, providing a low-friction surface between two sliding parts. They’re like the behind-the-scenes crew in a blockbuster movie, making everything look seamless without stealing the limelight. While other bearings roll or glide, plain bearings, also known as sleeve bearings, rely on a layer of lubrication to reduce friction. They’re commonly used in:
- Refrigeration: The quiet hum of your refrigerator can be attributed to plain bearings, which allow the compressor to run smoothly.
- Aircraft Engines: Plain bearings play a critical role in aircraft engines, keeping them operating at peak performance during long flights.
- Fittings & Bicycles: You’ll find plain bearings in hinges, door knobs, and even the pedals on your bicycle.
- Maintenance: Simply follow the usual maintenance procedures and raise a flag in case of any abnormalities in alignment, lubrication, etc.
Thrust Bearings: Handling the Pressure
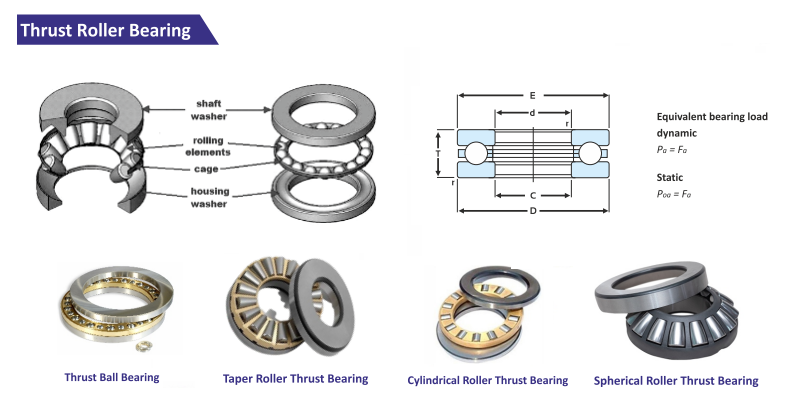
Imagine the intense competition in a game of chess, with each piece vying for dominance. Thrust bearings handle axial loads, like the strategic moves in chess, allowing machines to function smoothly under pressure. Think of thrust bearings as the referees of the bearing world. They handle axial loads, ensuring that components stay in their lanes. You can find them in:
- Wind Turbines: Thrust bearings keep wind turbine blades aligned with the wind, maximizing energy production from renewable sources.
- Power Tools: In your favorite DIY power drill, thrust bearings help transmit the force from the motor to the drill bit efficiently.
- Aeronautics: They are crucial in applications like helicopter rotors, ensuring precision and stability during flight.
- Maintenance: Regular lubrication is crucial to reduce friction and prevent wear. Monitor operating temperatures to detect potential issues early, and ensure that the bearing is properly aligned within its housing to prevent uneven wear. Regular inspections for signs of damage or contamination, along with prompt replacement of worn components, contribute to the overall longevity and optimal performance of thrust bearings.
Magnetic Bearings: The Futuristic Touch
Now, let’s step into the future with magnetic bearings. Taking a leap into the future, magnetic bearings use electromagnets to levitate a rotating shaft without any physical contact. Think of them as the hoverboards from “Back to the Future,” defying gravity and friction to achieve ultra-smooth and efficient rotation. These bearings use magnetic fields to levitate and move components, eliminating physical contact and friction. They’re used in:
- High-Speed Trains: Perfect for high-speed turbomachinery. Magnetic bearings help maintain the incredible speeds of trains like the Japanese Maglev, which can reach up to 375 mph!
- MRI Machines: The precision of magnetic bearings is vital in the medical field, ensuring the safety and accuracy of MRI scans.
- Maintenance: Regular monitoring of bearing temperatures, alignment, and vibration levels is essential to detect potential issues early. Implement a systematic lubrication schedule using the recommended lubricants to minimize friction and wear. Conduct routine inspections for any signs of contamination or damage to the bearing surfaces.
Ceramic Bearings: The Tough and Resilient Ones
Ceramic bearings, made from materials like silicon nitride, are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. These bearings are tough cookies and are perfect for high impact applications.
- High-performance sports equipment: Skateboards, inline skates, and high-speed fishing reels.
- Wind Turbine: To be able to put up with the pressure and resistance.
- Steel Rolling Mills: For handling heavy duty metal works with complete finesse.
- Maintenance: Maintaining ceramic bearings involves stringent cleanliness protocol during installation and handling to prevent particle ingress that could compromise performance. Adhering to these maintenance practices enhances the durability, efficiency, and reliability of ceramic bearings.
Hydrostatic Bearings: Gliding on a Cushion of Fluid
Imagine a hovercraft gliding effortlessly on a cushion of air—hydrostatic bearings work similarly, using a pressurized fluid to lift and support heavy loads. Hydrostatic bearings are prized for their ability to provide ultra-precise positioning, reduce friction and wear, dampen vibrations, and handle heavy loads. These qualities make them invaluable in industries where accuracy, reliability, and efficiency are paramount.
- Machine Tools: High-precision machine tools, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and machining centers. They offer exceptional stability, vibration dampening, and high precision during metalworking processes, ensuring the production of accurate and finely finished components.
- Metrology and Calibration: Coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical inspection systems, rely on hydrostatic bearings for their precision and repeatability. These bearings help ensure accurate measurements and quality control in various industries.
To wrap up, in the grand scheme of things, bearings are the unsung heroes that keep the wheels of progress turning. Bearings play a vital role in countless applications, making our lives easier and more efficient. So, the next time you hop on a train, open your fridge or take a spin on your bicycle, take a moment to appreciate the magic of bearings – the true champions of friction reduction, quietly keep the show running, one smooth rotation at a time..










